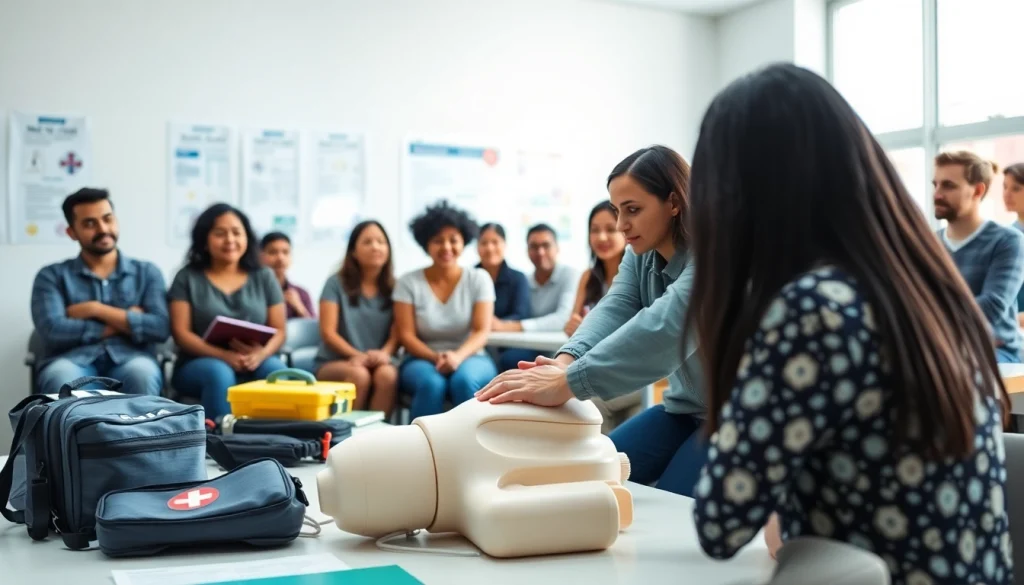
Understanding the Importance of First Aid
First Aid is a critical skill that can mean the difference between life and death in emergencies. Knowing how to respond when an accident occurs or an illness manifests is invaluable. Whether you are at home, at work, or on the road, being equipped with the knowledge of First Aid can empower you to act swiftly and effectively in potentially life-threatening situations. Understanding the fundamentals of First Aid not only enhances your confidence but also contributes to a safer community. To explore more about effective First Aid practices, you might find valuable resources at First Aid.
What is First Aid?
First Aid refers to the initial assistance or treatment provided to someone suffering from a minor or serious illness or injury. The main goal of First Aid is to preserve life, prevent further injury, and promote recovery. It encompasses a variety of techniques that include assessing a person’s condition, stabilization, and providing necessary care until professional medical services arrive.
Why Every Individual Should Know First Aid
First Aid knowledge is not limited to healthcare professionals; it is essential for every individual. The ability to deliver immediate care can be crucial during emergencies. Every second count when someone is injured. Knowing how to administer First Aid can help reduce recovery times and potentially save lives, providing peace of mind for yourself and others.
Additionally, First Aid training encourages responsibility and awareness of health and safety issues. It empowers individuals to create safer environments at home, in schools, and at workplaces, fostering a culture of care and readiness.
Common Misconceptions About First Aid
Despite its importance, there are several misconceptions surrounding First Aid. One common myth is that only trained professionals can provide effective First Aid. In reality, anyone can learn and apply basic First Aid techniques. Another misconception is that First Aid is only necessary in severe emergencies. However, First Aid also involves addressing minor issues like cuts, bruises, and burns—situations that frequently occur in everyday life.
Additionally, many believe that administering First Aid will interfere with the arrival of medical professionals. In fact, First Aid can stabilize a person’s condition and assist in better treatment once professionals take over. Recognizing these misconceptions fosters a more proactive approach to safety and preparedness.
Basic First Aid Techniques Everyone Should Learn
Recognizing and Responding to Emergencies
The first step in any emergency is to assess the scene for safety. Before you intervene, ensure that it is safe for you to approach the victim. Look for potential dangers like traffic, fire, or unstable structures. If it is safe, proceed to check the individual’s responsiveness—call their name loudly or gently shake their shoulder. If they do not respond, it may be time to call for emergency help.
After ensuring safety and responsiveness, it’s crucial to check for breathing and circulation. If necessary, begin administering CPR and other necessary First Aid techniques.
Administering CPR: A Step-by-Step Approach
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is one of the most critical First Aid techniques everyone should know. To perform CPR effectively, follow these steps:
- Call for emergency help immediately.
- Ensure the person is on a firm, flat surface. Position yourself next to their side.
- Check for breathing for no more than 10 seconds. If the person is not breathing normally, proceed.
- Place the heel of one hand on the center of the person’s chest, with the other hand on top, interlocking the fingers. Keep your elbows straight.
- Compress the chest at least 2 inches deep, at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. Allow the chest to fully rise between compressions.
- After every 30 compressions, give 2 rescue breaths, pinching the nose, sealing your mouth over theirs, and breathing into their mouth until you see their chest rise.
- Continue the cycle of 30 compressions and 2 breaths until emergency help arrives or the person starts to show signs of life.
CPR can double or triple a victim’s chances of survival in emergencies involving cardiac arrest, making it a crucial skill to master.
Wound Care and Control of Bleeding
Wound care is essential for preventing infection and managing bleeding. Here are the fundamental steps for treating wounds:
- Wash your hands thoroughly before tending to the wound.
- Apply gentle pressure to stop any bleeding with a clean cloth or bandage.
- Once bleeding stops, clean the wound with mild soap and clean water. Avoid getting soap in the wound.
- Apply an antibiotic ointment and cover with a sterile bandage or dressing.
- Monitor the wound for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus.
In cases of severe bleeding that does not stop with direct pressure, elevate the injury above the level of the heart and seek emergency medical help immediately.
First Aid Kits: What You Need to Know
Essential Items in a First Aid Kit
A well-stocked First Aid kit is fundamental for providing quick assistance during emergencies. Here are some essential items to include:
- Adhesive bandages in various sizes
- Gauze pads and adhesive tape
- Antiseptic wipes and antibiotic ointment
- Scissors and tweezers
- Disposable gloves
- Instant ice packs
- CPR face shield or mask
- Thermometer
- Pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen, acetaminophen)
It’s important to inspect your First Aid kit regularly, ensuring that supplies are in good condition and medications have not expired.
Customizing Your First Aid Kit for Specific Needs
While a general First Aid kit covers basic needs, consider customizing your kit based on specific activities or environments. For instance:
- If you frequently hike, add items like sunscreen, insect repellent, and extra hydration supplies.
- For families with young children, include pediatric-sized bandages, antiseptics suitable for children, and any necessary medications for allergies or conditions.
- In workplaces, integrate items specific to common risks associated with job activities, such as splints for fractures or special dressings for burns.
Customizing ensures that you are prepared for the unique challenges you may face in different situations.
Where to Keep Your First Aid Kit
The placement of your First Aid kit is as critical as its content. Keep your kit in accessible locations, ensuring that all family members or colleagues know where to find it. Here are some recommendations for storage:
- At home, store the kit in a kitchen drawer or on a shelf that is easily reachable.
- In a vehicle, keep the First Aid kit in the glove compartment or console but ensure it is secured to prevent movement during driving.
- In workplaces, designate a specific area for the First Aid kit, and make sure it is clearly marked.
Review the location periodically to ensure it remains accessible and stocked.
Advanced First Aid Techniques for Lifesaving Situations
Managing Choking Incidents
Choking is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate action. To assist someone who is choking, remember to follow these steps:
- Encourage the person to cough if they can still breathe. This may help dislodge the obstruction.
- If the person cannot cough, breathe, or speak, stand behind them and wrap your arms around their waist.
- Make a fist with one hand, positioning it just above the person’s navel. Grasp it with your other hand and thrust inward and upward quickly.
- Continue this technique until the object is expelled or the individual becomes unresponsive.
If they become unresponsive, lower them to the ground and begin CPR, checking the mouth for any visible obstructions before rescue breaths.
Using a Defibrillator: A Quick Guide
Automated External Defibrillators (AED) are essential tools in sudden cardiac arrest situations. Knowing how to use an AED can significantly increase the chances of survival. Here’s how to use one:
- Call for emergency medical services immediately.
- Turn on the AED and follow the voice prompts provided.
- Expose the person’s chest and apply the adhesive pads as indicated on the device.
- Ensure no one is touching the person and press the button to deliver a shock if advised by the AED.
- Continue CPR until the AED prompts you otherwise.
Defibrillators are designed to be used by laypersons, with clear instructions that make them accessible and easy to operate.
Recognizing Signs of Shock and How to Help
Shock occurs when the body doesn’t get enough blood flow, which can lead to organ failure and death. Recognizing the signs of shock is crucial:
Symptoms may include:
- Pale, clammy skin
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Weak and rapid pulse
- Dizziness or fainting
To assist someone in shock:
- Call emergency services immediately.
- Have the person lie down and elevate their legs to promote blood flow to vital organs.
- Keep them calm and warm, and reassure them help is on the way.
- Avoid giving them food or drink, as this can complicate future medical treatment.
Timely recognition and response to shock can significantly improve outcomes.
First Aid Training Resources and Certifications
Finding Quality First Aid Training Courses
Accessing high-quality First Aid training is paramount for acquiring essential life-saving skills. Here are a few avenues for finding certified courses:
- Local health organizations often offer courses that cover basic and advanced techniques.
- Community colleges and adult education programs frequently provide First Aid training as part of their health education curriculum.
- Online platforms offer flexible training options that can be tailored to your schedule.
Before enrolling, ensure the course is certified by recognized authorities such as the American Red Cross or the National Safety Council.
Preparing for Certification: Tips and Resources
Certification in First Aid provides formal recognition of your skills and knowledge. To prepare effectively:
- Choose a course that suits your needs, whether it’s basic First Aid, CPR, or specialized training such as wilderness First Aid.
- Familiarize yourself with the materials and guidelines provided by the training organization.
- Practice regularly with friends or colleagues to reinforce your skills.
- Be prepared to take both written and practical assessments to demonstrate your proficiency.
Certification often requires renewal every few years, so staying engaged in ongoing training is beneficial.
Keeping Your Skills Updated and Practiced
First Aid is a skill that requires regular practice to maintain proficiency. Here’s how you can keep your skills sharp:
- Participate in refresher courses annually to stay current with new techniques and guidelines.
- Review First Aid manuals and online resources available from reputable organizations.
- Engage in community drills or training sessions that simulate emergency scenarios.
- Share knowledge and experiences with peers, as teaching others can enhance your understanding.
Continual learning and practice ensure that you are always prepared to act effectively in emergencies.